WebDAV
You can connect to any WebDAV compliant server using both HTTP and HTTP/SSL. Mutual TLS with a client certificate for authentication is supported.
Providers
Settings are specific to service providers.
Note
Connection profiles can be installed from Preferences → Profiles.
Supported Authentication Methods
HTTP Basic Authentication
Basic Authentication should only be used when using a secured connection over TLS (HTTPS).
HTTP Digest Authentication
Both HTTP Basic Authentication and Digest Authentication are supported.
NTLM Authentication
When connecting to a SharePoint WebDAV server.
Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA)
Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) is a Microsoft technology that allows users to automatically authenticate using Windows credentials without needing to manually enter a username and password. Supported using NTLM authentication protocol.
Download
and use the WebDAV (Integrated Windows Authentication) profile to connect to the server using Integrated Windows
Authentication.
SSL/TLS Support
Choose WebDAV (HTTP/SSL) as the connection protocol to secure the connection using SSL. Interoperable with TLSv1.3 and TLSv1.2.
TLSv1 and TLSv1.1 deprecation
TLSv1 and TLSv1.1 are no longer supported as of
Mutual TLS (mTLS)
Mutual (two-way) TLS with a client certificate for authentication is supported.
Prompt to Authenticate with Certificate When Negotiating Secure (TLS) Connection
When a server requests a client certificate for authentication, a prompt is displayed to choose a certificate with a private key that matches the given issuer name requested from the server. Matching certificates are searched for in the Keychain on macOS or the Windows Certificate Manager respectively.
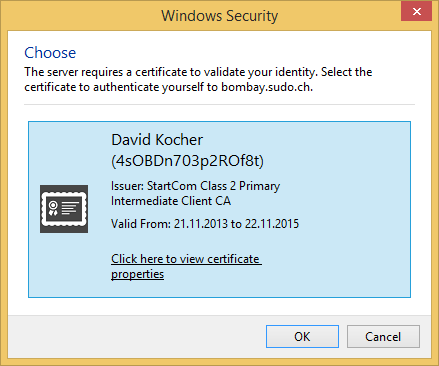
Select Client Certificate in Bookmark
You can also pre-select a certificate to use for authentication when editing the bookmark.
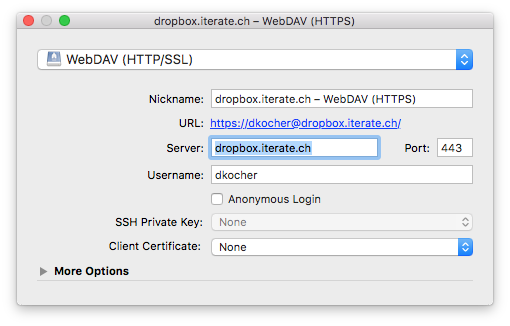
Trust Certificate
If the certificate is not trusted by the system, you are asked to make an exception if you still want to connect to the site that cannot be verified. This failure during certificate trust verification is most often the case when the certificate is invalid either
Because the hostname does not match the common name in the certificate. You will get the error message You might be connecting to a server that is pretending to be….
The certificate is self-signed or signed by a root authority not trusted in the system.
The certificate is expired.
You can temporarily or permanently allow connecting nevertheless by choosing Continue. To remember your choice, select Always Trust….
Metadata
You can edit custom properties using File → Info → Metadata.
Locking
Locking is not supported editing with Cyberduck.
Mountain Duck supports locking using LOCK and UNLOCK methods when opening documents for editing. Refer
to File Locking.
Distribution (CDN)
You can enable custom origin Amazon CloudFront (Content Delivery Network) distribution using File → Info → Distribution (CDN).
Known Issues
Modification Date
Saving the modification dates requires support from server storing metadata in custom namespace.
Cannot Login with Special Characters in Credentials
If your server requires the use of UTF-8 character set for authentication, set the hidden configuration option
http.credentials.encoding=UTF-8
Too Many Folders are Displayed
Attention
This only applies if you access a Synology Diskstation.
If the file listing shows additional folders of the file tree that are usually not visible try to uncheck the checkbox disable directory browsing within the advanced settings for a shared folder on your Synology Diskstation.
Interoperability Failure Handshake alert: unrecognized_name
The virtual host set up by the hosting provider is most possibly misconfigured. It must accept TLS connections with
SNI (Server Name Indication) extension (RFC 4366). The hostname must match the common name in the server certificate. In
Apache httpd configurations, add a ServerAlias configuration directive with the hostname you use to connect.
You can verify the wrong server setup by running openssl with server name indication (SNI) enabled.
openssl s_client -servername <servername> -tlsextdebug -msg -connect <servername>:443
This will print
<<< TLS 1.0 Alert [length 0002], warning unrecognized_name
during the handshake, if there is a configuration problem.
See also Cyberduck Issue #7908.
Disable Expect: 100-continue
The Expect: 100-continue to make sure a server accepts an upload before data is sent. You can disable the use of this
feature when there is an interoperability issue by setting
the hidden option webdav.expect-continue to false.
Socket Timeout With GZIP Content Encoding
Some servers (cPanel) have invalid return GZIP encoded content. This error may not be seen with other clients that do
not enable content compression. An invalid HTTP response status line is sent and the content size does not match the
content length set. As a workaround, you can disable support for content compression. Set
the hidden option http.compression.enable to false.
Require Directive in Apache HTTPD
The Require directive in Apache HTTPD tests whether an authenticated user is authorized according to a particular
authorization provider and the specified restrictions. You should configure it to return a 403 HTTP status code when
authorization fails using the AuthzSendForbiddenOnFailure directive. Refer
to mod_authz_core.
Tip
If authentication succeeds but authorization fails, Apache HTTPD will respond with an HTTP response code of 401 UNAUTHORIZED by default. This usually causes browsers to display the password dialogue to the user again, which is not
wanted in all situations. AuthzSendForbiddenOnFailure allows changing the response code to 403 Forbidden.
0 Byte Files on WebDAV Server
If you are running an Apache configuration make sure to disable fastcgi and php-fpm. Refer to
our best practice for Nextcloud and ownCloud installations.
mod_evasive
Deployments with WebDAV on Apache HTTP server with the mod_evasive module may block requests leading to permission
failures with 403 HTTP errors returned by the server.
Interoperability with Microsoft IIS
The following configuration options are recommended for interoperability. Refer to IIS Manager to configure these settings.
Enable
HEADmethodEnable double escaping
Disable Filter Double-Encoded Requests