Amazon S3

Transfer files to your S3 account and browse the S3 buckets and files in a hierarchical way.
Connecting
You must obtain the login credentials (Access Key ID and Secret Access Key) of your Amazon Web Services Account from the AWS Access Identifiers page. Enter the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key in the login prompt.
IAM User
You can also connect using IAM credentials that have the Amazon S3 Full Access template
policy permissions attached and optionally the CloudFront Full Access.
Generic S3 Profiles
Note
Connection profiles for use with third-party S3 installations can be installed from Preferences → Profiles.
Authentication with signature version AWS4-HMAC-SHA256
Important
It is discouraged to enable this option to connect plaintext to Amazon S3.
If you have an S3 installation without SSL configured, you need an optional connection profile to connect using HTTP only without transport layer security. You will then have the added option S3 (HTTP) in the protocol dropdown selection in the Connection and Bookmark panels.
Downloadthe S3 (HTTP) profile for preconfigured settings.S3 (HTTPS) profile bundled by default.
Authentication with signature version AWS2
Attention
Connection profiles using legacy AWS2 signature authentication are not recommended to be used with AWS S3 as some regions and features like Key Management Service and CloudFront configuration are not supported.
S3 GovCloud (US-East)
Use the endpoint s3.us-gov-east-1.amazonaws.com or install the connection profile
Downloadthe S3 GovCloud ( US-East) profile for preconfigured settings.
S3 GovCloud (Us-West)
Use the endpoint s3.us-gov-west-1.amazonaws.com or install the connection profile
Downloadthe S3 GovCloud ( US-West) profile for preconfigured settings.
Connect to the region AWS China (Beijing)
**Connect to S3 interface VPC endpoint **
Downloadthe AWS PrivateLink for Amazon S3 (VPC endpoint) profile.
Connecting to a Single Bucket
Connecting to a bucket owned by you or even a third party is possible without requiring permission to list all buckets. You can access buckets owned by someone else if the ACL allows you to access it by either:
Specify the bucket you want to access in the hostname to connect to like
<bucketname>.s3.amazonaws.com. Your own buckets will not be displayed but only this bucket contentsSet the Default Path in the bookmark to the bucket name. If you have permission you can still navigate one level up to display all buckets if the ACL allows.
Attention
No regional endpoint should be set while connecting to a single bucket. The endpoint will be determined automatically by querying the region of the bucket.
Connecting to a Public Bucket
To access public buckets with no access key required, you can choose Anonymous Login instead of providing Access Key ID and Secret Access Key.
Connecting using Deprecated Path Style Requests
For S3 compatible storage only supporting path style requests to reference buckets. Connect with a connection profile disabling virtual host style requests.
Downloadthe S3 (Deprecated path style requests) profile for preconfigured settings.
Alternatively set the hidden configuration option
s3.bucket.virtualhost.disable to true.
Interoperability
Attempting to connect using the regular S3 connection profile to a server with no support for virtual host style
requests will cause the error Cannot read container configuration with the message DNS is the network service that
translates a server name to its Internet address. This error is most often caused by having no connection to the
Internet or a misconfigured network. It can also be caused by an unresponsive DNS server or a firewall preventing access
to the network.
Connecting with OpenID Connect (OIDC) Identity Provider
Connecting to AWS S3 with web identity federation using AWS Security Token Service (STS) is supported with connection profiles specifying configuration properties specific to your identity provider (IdP).
Attention
The usage of these connection profiles requires the configuration of an OpenID Connect (OIDC) identity provider and role and trust policy in AWS IAM.
The connection profiles connect using temporary security credentials from the AWS Security Token Service (STS) obtained using a web identity token from your OpenID Connect (OIDC) identity provider. Refer to Custom connection profile using OpenID Connect provider and AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity STS API.
Interoperability
AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity API from AWS Security Token Service (STS) is used to exchange the JSON Web Token with
temporary security credentials. In addition to AWS, the following combinations of S3 & STS APIs with OpenID Connect (
OIDC) have been tested:
Connect to MinIO S3 authenticating with MinIO STS and Keycloak (OIDC)
Connect to AWS S3 authenticating with AWS STS and Keycloak (OIDC)
Connecting with Temporary Access Credentials (Token) from EC2
If you are running Cyberduck for Windows or Cyberduck CLI on EC2 and have
setup IAM Roles for Amazon EC2 to
provide access to S3 from the EC2 instance, you can use the connection profile below that will fetch temporary
credentials from EC2 instance metadata service at
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/s3access to authenticate. Edit the profile to change
the role name s3access to match your IAM configuration.
Downloadthe S3 (Credentials from Instance Metadata) profile for preconfigured settings
Connecting Using Credentials from AWS Command Line Interface
Instead of providing Access Key ID and Secret Access Key, authenticate using credentials managed in ~/aws/credentials
on macOS or %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials on Windows using third-party tools.
Downloadthe S3 (Credentials from AWS Command Line Interface) profile for preconfigured settings.
You must provide configuration in the standard credentials property file ~/.aws/credentials on macOS or
%USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials on Windows as well as the config file ~/aws/config on macOS or
%USERPROFILE%\.aws\config on Windows
from AWS Command Line Interface.
Configure a bookmark with the field titled Profile Name in ~/.aws/credentials matching the profile name from
~/.aws/credentials on macOS or %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials on Windows. The properties aws_access_key_id,
aws_secret_access_key and aws_session_token are supported.
Tutorial
Follow the step-by-step instructions to require MFA by assuming a role to access S3.
AWS IAM Identity Center
For a SSO connection authenticating with AWS IAM Identity Center (Successor to AWS Single Sign-On), the properties
sso_start_url, sso_account_id, and sso_role_name are required within the standard credentials property file
~/.aws/credentials (macOS) or %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials (Windows). The access key, secret key, and session
token cached by AWS CLI are retrieved from ~/.aws/cli/cache on macOS or %USERPROFILE%\.aws\cli\cache on Windows.
To populate the correct cache locations follow these steps:
Run the command
aws sso loginto populate~/.aws/sso/cacheon macOS or respectively%USERPROFILE%\.aws\sso\cacheon Windows. This adds client secrets but doesn’t add any usable AWS credentials.Seed the second cache in
~/.aws/cli/cacheon macOS or respectively%USERPROFILE%\.aws\cli\cacheon Windows by running the commandaws sts get-caller-identity. This adds the usable credentials to the location Cyberduck and Mountain Duck reads from.
Note
You can also do this for a specific profile by adding --profile myProfile to the commands. Make sure to use the same
profile for both steps.
Connecting Using AssumeRole from AWS Security Token Service (STS)
Tutorial
Follow the step-by-step instructions to require MFA with a user policy and connect by assuming a role from AWS Security Token Service (STS) granting access to S3.
Tutorial
Follow the step-by-step instructions to require MFA with a bucket policy and connect using a session token from AWS Security Token Service (STS).
Instead of providing Access Key ID and Secret Access Key, authenticate using temporary credentials from AWS Security Token Service (STS) with optional Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Refer to Using IAM Roles.
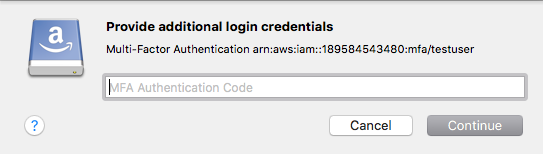
Downloadthe AWS S3 (STS AssumeRole) profile for preconfigured settings.Downloadthe AWS S3 (MFA Session Token) profile for preconfigured settings.Downloadthe S3 (Credentials from AWS Command Line Interface) profile to connect with settings from AWS CLI. You must provide configuration in the standard credentials property file~/.aws/credentialson macOS or%USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentialson Windows from AWS Command Line Interface. Configure a bookmark with the field titled Profile Name in~/.aws/credentialsmatching the profile name from~/.aws/credentialson macOS or%USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentialson Windows with therole_arnconfiguration.Example Configuration
Refer to Assuming a Role.
[testuser] aws_access_key_id=<access key for testuser> aws_secret_access_key=<secret key for testuser> [testrole] role_arn=arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/testrole source_profile=testuser mfa_serial=arn:aws:iam::123456789012:mfa/testuser
Read Credentials from ~/.aws/credentials
When editing a bookmark, the Access Key ID is set from the default profile in the credentials file located at
~/.aws/credentials on macOS or %USERPROFILE%\.aws\credentials on Windows if such a profile exists or the profile name matching the .
Connecting Without Using AWS credentials
Use the S3 (HTTPS) connection profile to access public data sets on AWS Open Data without using access keys by using the Anonymous Login option in the bookmark configuration.
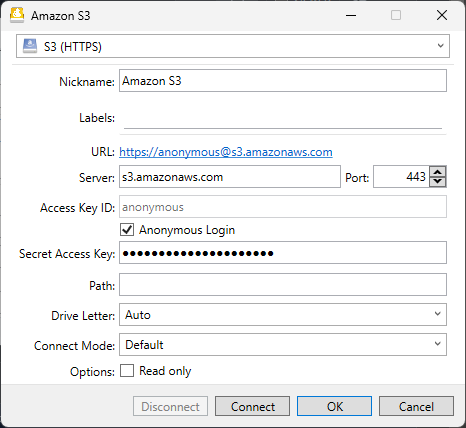
Downloadthe S3 (HTTPS) profile for preconfigured settings
Cyberduck CLI
List all buckets with Cyberduck CLI using
duck --username <Access Key ID> --list s3:/
List the contents of a bucket with
duck --username <Access Key ID> --list s3:/<bucketname>/
Refer to the Cyberduck CLI documentation for more operations.
Uploads Using CLI
Add default metadata for uploads using the preferences option to read from the environment. The property is documented in Default metadata.
env "s3.metadata.default=Content-Type=application/xml" duck --upload …
Set a default ACL for the upload with
env "s3.acl.default=public-read" duck --upload …
Buckets
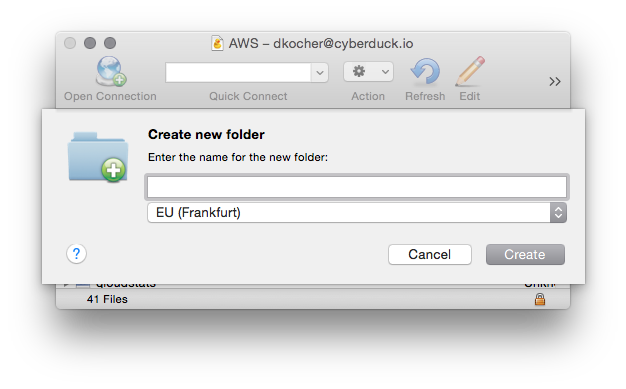
Creating a Bucket
To create a new bucket for your
account, browse to the root and choose File → New Folder… (macOS ⌘N Windows Ctrl+Shift+N). You can choose the
bucket location in Preferences (macOS ⌘, Windows Ctrl+,) → S3. Note that Amazon has a different pricing scheme for
different regions.
Mountain Duck
You will receive a prompt for the region when creating a new bucket
Supported Regions
EU (Ireland)
EU (London)
EU (Paris)
EU (Stockholm)
US East (Northern Virginia)
US West (Northern California)
US West (Oregon)
Asia Pacific (Singapore)
Asia Pacific (Tokyo)
South America (São Paulo)
Asia Pacific (Sydney)
EU (Frankfurt)
US East (Ohio)
Asia Pacific (Seoul)
Asia Pacific (Mumbai)
Canada (Montreal)
China (Beijing)
China (Ningxia)
Important
Because the bucket name must be globally unique the operation might fail if the name is already taken by someone else (E.g. don’t assume any common name like media or images will be available).
You cannot change the location of an existing bucket.
Bucket Access Logging
When this option is enabled in the S3 panel of the Info (File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return)) window for a
bucket or any file within, available log records for this bucket are periodically aggregated into log files and
delivered to /logs in the target logging bucket specified. It is considered best practice to choose a logging target
that is different from the origin bucket.
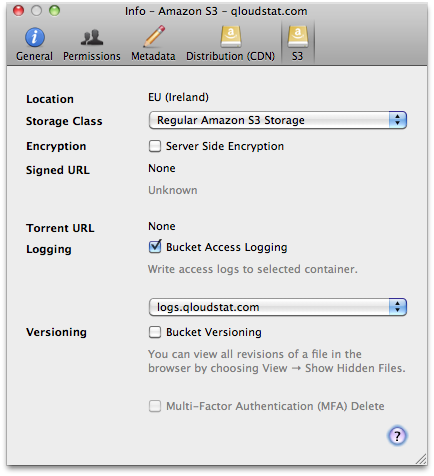
To toggle CloudFront access logging, select the the Distribution panel in the
File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) window.
Requester Pays Buckets
Per default, buckets are accessed with the parameter x-amz-requester-payer in the header to allow access to files in
buckets with the Requester Pays option enabled.
You can change the parameter using the following hidden configuration options.
s3.bucket.requesterpays=true
Versions
Versioning can be enabled per bucket in File → Info (macOS ⌘I
Windows Alt+Return) → S3. Make sure the user has the following permissions:
s3:PutBucketVersioningto permit users to modify the versioning configuration of a bucket.s3:GetBucketVersioningands3:ListBucketVersionsto see versions of a file.s3:GetObjectVersionto download a specific version.
You can view all revisions of a file in the browser by choosing View → Show Hidden Files.
Info → Versions
A list of file versions can be viewed in the Versions tab of the Info window. Files can be reverted to a chosen version of this list. Additionally, versions of the list can be deleted.
Revert
To revert to a previous version and make it the current, choose File → Revert.
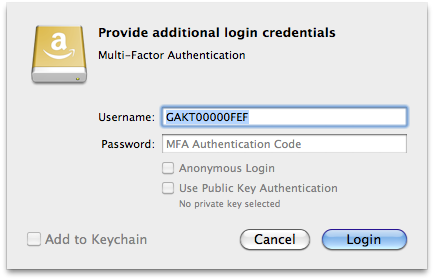
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Delete
To enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Delete, you need to purchase a
compatible authentication device. Toggle MFA in File → Info (macOS ⌘I
Windows Alt+Return) → S3. When enabled, you are prompted for the device number and one-time token in the login
prompt. Never reenter a token in the prompt already used before. A token is only valid for a single request. Wait for
the previous token to disappear from the device screen and request a new token from the device.
References
Folders
Creating a folder inside a bucket will create a placeholder object named after the directory, has no data content, and
the MIME type application/x-directory. This is interoperable with folders created
with AWS Management Console.
Important
Do not name objects in S3 containing / as this will break navigation.
File Transfers
Transfer Acceleration
When enabled for the bucket, downloads and uploads use the S3 Transfer Acceleration endpoints to transfer data through the globally distributed edge locations of AWS CloudFront.
Warning
The name of the bucket used for Transfer Acceleration must be DNS-compliant and must not contain periods (“.”).
Important
You do not need to enter transfer accelerated endpoints manually. When using Transfer Acceleration, additional data
transfer charges may apply to connect to s3-accelerate.dualstack.amazonaws.com.
Note
Make sure the IAM user has the s3:GetAccelerateConfiguration permission required to query the Transfer Acceleration
status of a bucket.
Checksums
Files are verified both by AWS when the file is received and compared with the SHA256 checksum sent with the request.
Additionally, the checksum returned by AWS for the uploaded file is compared with the checksum computed locally if
enabled in Transfers → Checksum → Uploads → Verify checksum.
Multipart Uploads
Files larger than 100MB are uploaded in parts with up to 10 parallel connections as 10MB parts. Given these sizes, the file size limit is 100GB with a maximum of 10’000 parts allowed by S3. The number of connections used can be limited using the toggle in the lower right of the transfer window.
Note
Multipart uploads can be resumed later when interrupted. Make sure the IAM user has the permission
s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads.
Unfinished Multipart Uploads
You can view unfinished multipart uploads in the browser by choosing View → Show Hidden Files.
Options
You can set options with the following hidden configuration options.
Part size for multipart uploads
s3.upload.multipart.size=10485760
Threshold to use multipart uploads is set to 100MB by default
s3.upload.multipart.threshold=104857600
Storage Class
You have the option to store files using the Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS) by storing non-critical, reproducible
data at lower levels of redundancy. Set the default storage class in Preferences (macOS ⌘, Windows Ctrl+,) → S3
and edit the storage class for already uploaded files using File → Info (
macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → S3. Available storage classes are
Regular Amazon S3 Storage
Intelligent-Tiering
Standard IA (Infrequent Access)
One Zone-Infrequent Access
Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS)
Glacier
Glacier Deep Archive
Tip
As the storage class applies to files selectively, it cannot be set as a default on a bucket. Therefore the storage class is displayed as Unknown for buckets.
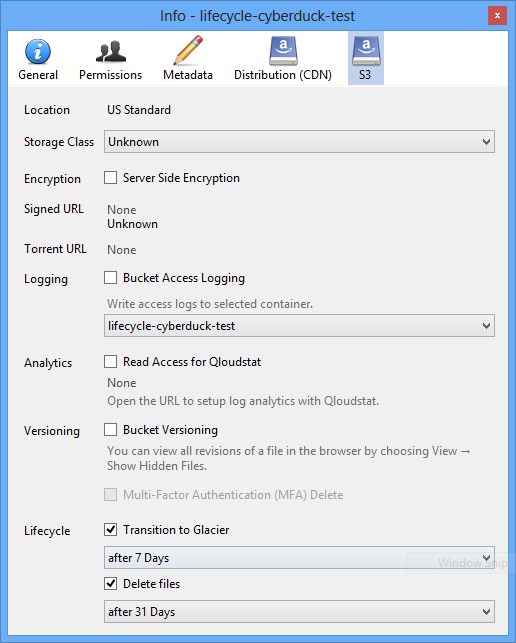
Lifecycle Configuration
Specify after how many days a file in a bucket should be moved to Amazon Glacier or deleted.
Restore from Glacier
Attention
This feature is currently Cyberduck only.
You can temporarily restore files from Glacier and Glacier Deep Archive using File → Restore. The file will be restored using standard retrieval and expire 2 days after retrieval. Restoring takes some time and attempting to download an item not yet restored will lead to an error The operation is not valid for the object’s storage class.
Glacier Retrieval Options
You can set retrieval options for the storage classes Glacier and Glacier Deep Archive with the following hidden configuration options.
Set Glacier retrieval tier at which the restore will be processed. Valid values are
Standard,BulkandExpedited.s3.glacier.restore.tier=Standard
Set the time, in days, between when an object is uploaded to the bucket and when it expires.
s3.glacier.restore.expiration.days=2
Mountain Duck
Temporarily restored files from Glacier won’t change the storage class and are not shown in Mountain Duck. To make restored Glacier files available for retrieval in Mountain Duck, make sure to change the storage class in Info → S3 of Cyberduck.
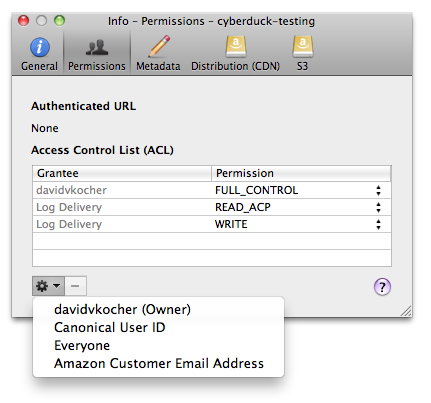
Access Control (ACL)
Amazon S3 uses Access Control List (ACL) settings to control who may access or modify items stored in S3. You can edit
ACLs in File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → Permissions. Alternatively, permissions can be changed
using bucket policies.
S3 Object Ownership
If you have
a bucket owner enforced policy set
with disabled ACLs for a bucket, it is required the IAM user
you connect with has permissions to read the bucket ownership controls. Ensure the user has
s3:GetBucketOwnershipControls permissions.
Canonical User ID Grantee
If you enter a user ID unknown to AWS, the error message S3 Error Message. Bad Request. Invalid id. will be displayed.
Email Address Grantee
If you enter an email address unknown to AWS, the error message S3 Error Message. Bad Request. Invalid id. will be
displayed. If multiple accounts are registered with AWS for the given email address, the error message
Bad Request. The e-mail address you provided is associated with more than one account. Please retry your request using a different identification method or after resolving the ambiguity.
is returned.
All Users Group Grantee
You must give the group grantee http://acs.amazonaws.com/groups/global/AllUsers read permissions for your objects to
make them accessible using a regular web browser for everyone.
If bucket logging is enabled, the bucket ACL will have READ_ACP and WRITE
permissions for the group grantee http://acs.amazonaws.com/groups/s3/LogDelivery.
Default ACLs
You can choose canned ACLs to be added to uploaded files or created buckets per default. Canned ACLs are predefined
sets of permissions.
The default ACL can be set within
Preferences (macOS ⌘, Windows Ctrl+,) → S3 → Default ACL.
Applies to buckets |
Applies to files |
|
|---|---|---|
|
✅ |
✅ |
|
✅ |
✅ |
|
✅ |
✅ |
|
✅ |
✅ |
|
❌ |
✅ |
|
❌ |
✅ |
You can disable the ACLs using the Amazon S3 Object Ownership.
Note
You need to set Preferences → S3 → Default ACL → None for uploads with disabled ACLs to succeed. Otherwise uploads
fail with The bucket does not allow ACLs..
Permissions
The following permissions can be given to grantees:
Bucket |
Files |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Allows grantee to list the files in the bucket |
Allows grantee to download the file and its metadata |
|
Allows grantee to create, overwrite, and delete any file in the bucket |
Not applicable |
|
Allows grantee all permissions on the bucket |
Allows grantee all permissions on the object |
|
Allows grantee to read the bucket ACL |
Allows grantee to read the file ACL |
|
Allows grantee to write the ACL for the applicable bucket |
Allows grantee to write the ACL for the applicable file |
Attention
You may receive an error Cannot change permissions of when attempting to grant Everyone READ permission for a file if the bucket has public access blocked because Block Public Access settings are turned on for this bucket.
Public URLs
You can access all URLs (including from CDN configurations) from the menu Edit → Copy URL and File → Open URL.
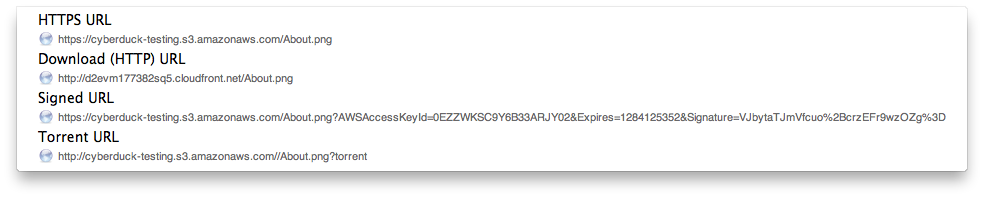
Important
Public URLs are only accessible if the permission READ is granted for EVERYONE.
Choose File → Share… to change the ACL on the file permanently allowing read for everyone. You can reset the changed ACL in Info → ACL.
Pre-signed Temporary URLs
A private object stored in S3 can be made publicly available for a limited time using a pre-signed URL. The pre-signed
URL can be used by anyone to download the object, yet it includes a date and time after which the URL will no longer
work. Copy the pre-signed URL from Edit → Copy URL→ Signed URL or File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) →
S3.
There are pre-signed URLs that expire in one hour, 24 hours (using the preference s3.url.expire.seconds), a week, and
a month. You can change the hidden preference
s3.url.expire.seconds from the default 86400 (24 hours).
Important
It is required that your AWS credentials are saved in keychain. Refer to Passwords.
Force use of AWS2 Signature
Using the AWS4 signature version used in Cyberduck 5 and later, pre-signed URLs cannot have an expiry date later than a week. You can revert by setting the default signature version to AWS2 by using the S3 AWS2 Signature Version (HTTP) connection profile.
Note
This deprecated signature version is not compatible with new regions such as eu-central-1.
Limitations
Share links cannot be created when failing to update the ACLs on a file because
Bucket has “Object Ownership” set to “Bucket owner enforced” (ACLs disabled). Error message:
This bucket does not allow ACLs“Block public access” is enabled on bucket. Error message:
Access denied
Metadata
You can edit standard HTTP headers and add custom HTTP headers to files
to store metadata. Choose File →
Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → Metadata to edit headers.
Default Metadata
Currently only possible using a hidden configuration option you can define
default headers to be added for uploads. Multiple headers must be separated using a whitespace delimiter. Key and value
of a header are separated with =. For example, if you want to add an HTTP header for Cache-Control and one named
Creator you would set
s3.metadata.default="Cache-Control=public,max-age=86400 Creator=Cyberduck"
Cache Control Setting
This option lets you control how long a client accessing objects from your S3 bucket will cache the content and thus
lowering the number of access to your S3 storage. In conjunction with Amazon CloudFront, it controls the time an object
stays in an edge location until it expires. After the object expires, CloudFront must go back to the origin server the
next time that edge location needs to serve that object. By default, all objects automatically expire after 24 hours
when no custom Cache-Control header is set.
The default setting is Cache-Control: public,max-age=2052000 when choosing to add a custom Cache-Control header in
the Info panel which translates to a cache expiration of one month (one month in seconds
equals more or less 60*60*24*30).
Use the hidden configuration option s3.cache.seconds to set a custom default
value
s3.cache.seconds=2052000
References
Tip
Use curl -I <http://<bucketname>.s3.amazonaws.com/<key> to debug HTTP headers.
Server Side Encryption (SSE)
Server-side encryption for stored files is
supported and can be enabled by default for all uploads in the S3 preferences or for individual files in the File →
Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → S3. AWS handles key management and key protection for you.
Defaults
Choose Preferences → S3 → Server Side Encryption to change the default.
None will not encrypt files (Default).
SSE-S3 will encrypt files using AES-256 with a default key provided by S3.
SSE-KMS will encrypt files with the default key stored in AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
You can override these default settings in the File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → S3 panel per bucket.
Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3)
When changing the setting for a folder or bucket you are prompted to confirm the recursive operation on all files contained in the selected bucket or folder.
Server-Side Encryption with AWS KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS)
Among the default SSE-S3 (AES-256), the server-side encryption (SSE) dropdown list allows choosing from all private
keys managed in AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
Permissions
This requires the kms:ListKeys and kms:ListAliases permission for the AWS credentials used to connect to S3.
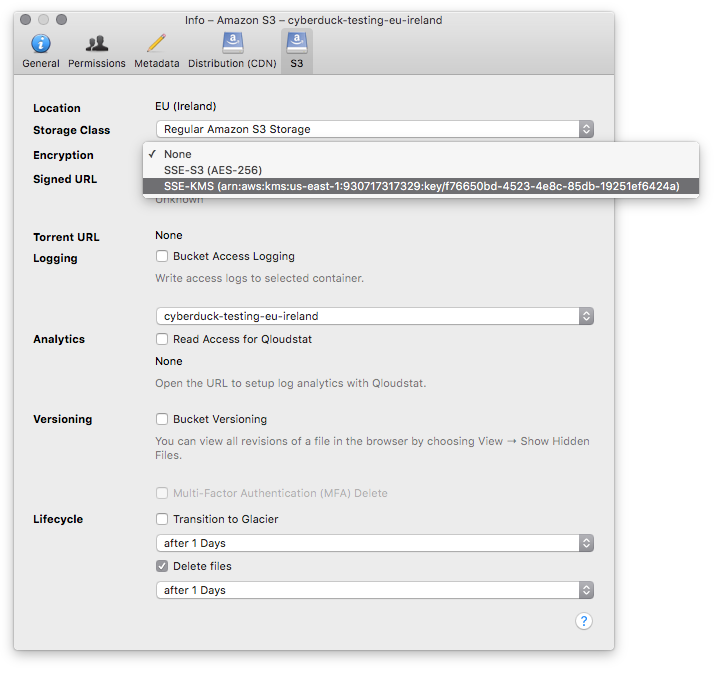
When changing the setting for a folder or bucket you are prompted to confirm the recursive operation on all files contained in the selected bucket or folder.
Prevent Uploads of Unencrypted Files
Refer to the AWS Security Blog
CloudFront CDN
Amazon CloudFront delivers your static and streaming content using a global network of edge locations. Requests for your objects are automatically routed to the nearest edge location, so content is delivered with the best possible performance. Refer to Amazon CloudFront distribution for help about setting up distributions.
Website Configuration
To host a static website on S3, It is possible to define an Amazon S3 bucket as a Website Endpoint. The configuration
in File → Info (macOS ⌘I Windows Alt+Return) → Distribution allows you to enable website configuration. Choose
Website Configuration (HTTP) from Delivery Method and define an index document name that is searched for and
returned when requests are made to the root or the subfolder of your website.
To access this website functionality, Amazon S3 exposes a new website endpoint for each region (US Standard, US West,
EU, or Asia Pacific). For example, s3-website-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com is the endpoint for the Asia Pacific
Region. The location is displayed in the Where field following the Origin.
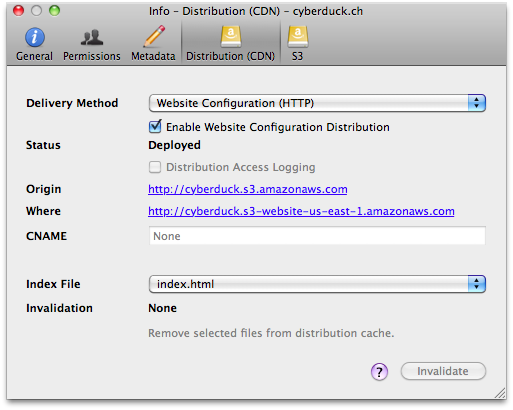
To configure Amazon CloudFront for your website endpoints, refer to Website Configuration Endpoint Distributions with CloudFront CDN.
References
Known Issues
Modification Date
The modification date retention is only supported using the {download}
S3 (Timestamps) profile<https://profiles.cyberduck.io/S3%20(Timestamps).cyberduckprofile>. When using this connection
profile, the modification and creation dates get written into the metadata in form of x-amz-meta-Mtime and
x-amz-meta-Btime for files uploaded to S3. .
Listing folders will require an additional HEAD request for every file to read the modification date from the object
metadata. This can cause performance issues due to the excessive number of requests required with large directory
contents.
Tip
Make sure to enable Preserve modification date in Preferences → Transfers → Timestamps in Cyberduck.
The S3 (Timestamps) profile is only
necessary if you want to view the timestamps set in the browser.
Interoperability
The timestamp metadata is interoperable with rclone.
Listing directory / failed. with Path in Custom S3 Endpoint
When connecting to a service that requires a path prefix in all requests, you must set the Context property in a
custom connection profile.
Moved Permanently but no Location Header
Make sure the IAM user has the permission s3:GetBucketLocation to read the bucket location.
Writing Files to S3 Compatible Third-Party Service Provider may Fail
The S3 interoperable service must support multipart uploads.
Delete Marker
When overwriting files some applications (like Windows File Explorer) will delete files prior to writing the new file. Thus we also forward this delete operation to S3 resulting in the delete marker being set. You can overwrite files with command-line tools which typically do not delete files prior to overwriting.
In Finder.app, Creating a new Top-Level Folder in S3 Fails with
Interoperability failure. Bucket name is not DNS compatible. Please contact your web hosting service provider for assistance.
A bucket name in S3 cannot have whitespace in the filename. Because a new folder created with Finder.app is named
Untitled Folder the operation fails. As a workaround, create a new bucket with mkdir in Terminal.app.
Note
The bucket can be created within the Smart Synchronization mode as the folder only gets uploaded after it is renamed. Make sure to choose a filename with no whitespace. For the additional restrictions of the bucket name, refer to the AWS bucket naming rules.
Saving a File in TextEdit.app will Attempt to Create a Folder
/Temporary Items on the Remote Volume. On some Servers, this may fail due to a Permission Failure or Because the Name
of the Folder is not Allowed as in S3.
You will get the error message
As of
Mountain Duck version 2.1, Bucket name is not DNS compatible. Please contact your web hosting service provider for assistance...DS_Store files are only saved in a temporary location and not stored on the mounted remote
volume.